3-7
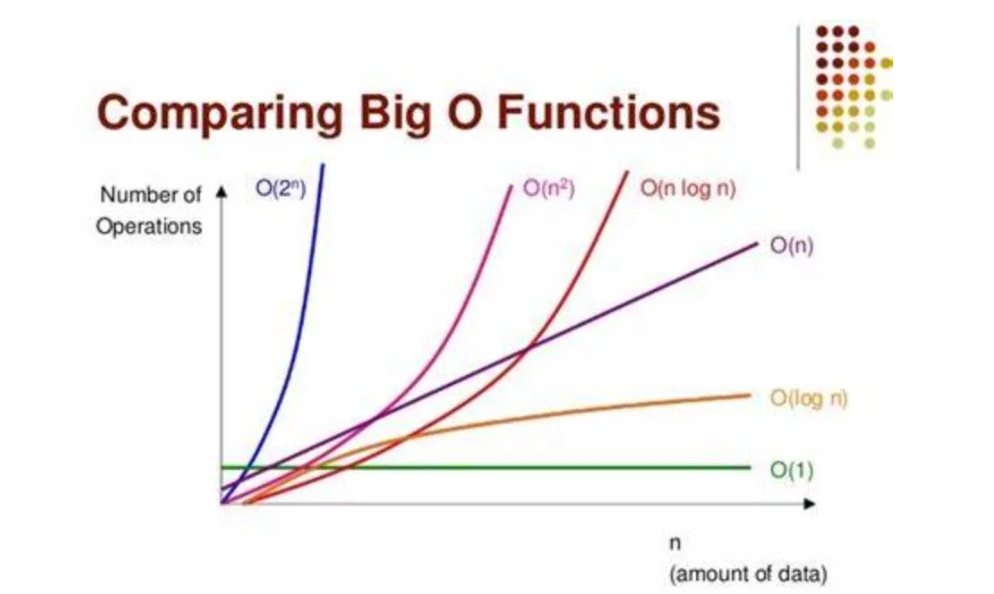
数据结构时间复杂度图

1 算法3.7
题目:76. 最小覆盖子串 ( 困难😟 )
标签:滑动窗口
给你一个字符串 s 、一个字符串 t 。返回 s 中涵盖 t 所有字符的最小子串。如果 s 中不存在涵盖 t 所有字符的子串,则返回空字符串 "" 。
注意:
- 对于
t中重复字符,我们寻找的子字符串中该字符数量必须不少于t中该字符数量。 - 如果
s中存在这样的子串,我们保证它是唯一的答案。
示例
示例 1:
输入:s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC"
输出:"BANC"
示例 2:
输入:s = "a", t = "a"
输出:"a"
示例 3:
输入: s = "a", t = "aa"
输出: ""
解释: t 中两个字符 'a' 均应包含在 s 的子串中,
因此没有符合条件的子字符串,返回空字符串。
分析
暴力法
滑动窗口
两个指针,l和r组成一个窗口,r向右移动直到覆盖所有t,此时向右移动l,直到最小串都覆盖t
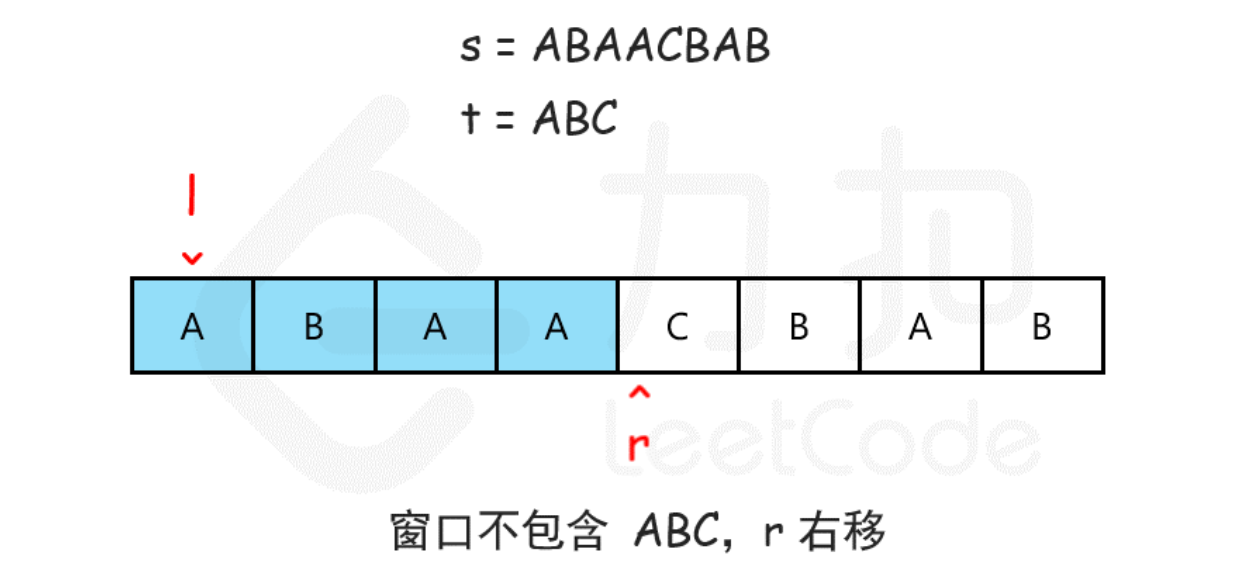
题解
function minWindow(s: string, t: string): string {
const ori = new Map<string, number>()
const cnt = new Map<string, number>()
const tLen = t.length
const sLen = s.length
for (let i = 0; i < tLen; ++i) {
const val = t.charAt(i)
ori.set(val, ori.get(val) ? ori.get(val) + 1 : 1)
}
let l = 0,
r = -1
let len = Infinity,
ansL = -1,
ansR = -1
while (r < sLen) {
++r
const val = s.charAt(r)
if (r < sLen && ori.has(val)) {
cnt.set(val, cnt.get(val) ? cnt.get(val) + 1 : 1)
}
while (check() && l <= r) {
if (r - l + 1 < len) {
len = r - l + 1
ansL = l
ansR = l + len
}
const val = s.charAt(l)
if (ori.has(val)) {
cnt.set(val, cnt.get(val) ? cnt.get(val) - 1 : -1)
}
++l
}
}
return len == Infinity ? '' : s.slice(ansL, ansR)
function check() {
let res = true
ori.forEach((val, key) => {
const cntVal = cnt.get(key) || 0
if (cntVal < val) {
return (res = false)
}
})
return res
}
}
使用
function main() {
const s = 'ADOBECODEBANC'
const t = 'ABC'
console.log('[]:', minWindow(s, t))
}
main()
2 算法3.8
题目:4. 寻找两个正序数组的中位数 ( 困难😟 )
给定两个大小分别为 m 和 n 的正序(从小到大)数组 nums1 和 nums2。请你找出并返回这两个正序数组的 中位数 。
算法的时间复杂度应该为 O(log (m+n)) 。
示例
示例 1:
输入:nums1 = [1,3], nums2 = [2]
输出:2.00000
解释:合并数组 = [1,2,3] ,中位数 2
示例 2:
输入:nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3,4]
输出:2.50000
解释:合并数组 = [1,2,3,4] ,中位数 (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5
分析
如果不需要满足 O(log (m+n)),则可以采用:
法一:合并数组,排序,找中位数
时间复杂度O((m+n)*log(m+n)),空间复杂度O(m+n)
法二:二分法合并数组,找中位数
时间复杂度O(m+n),空间复杂度O(m+n)
但如果要符合时间复杂度为 O(log (m+n)),有点难度
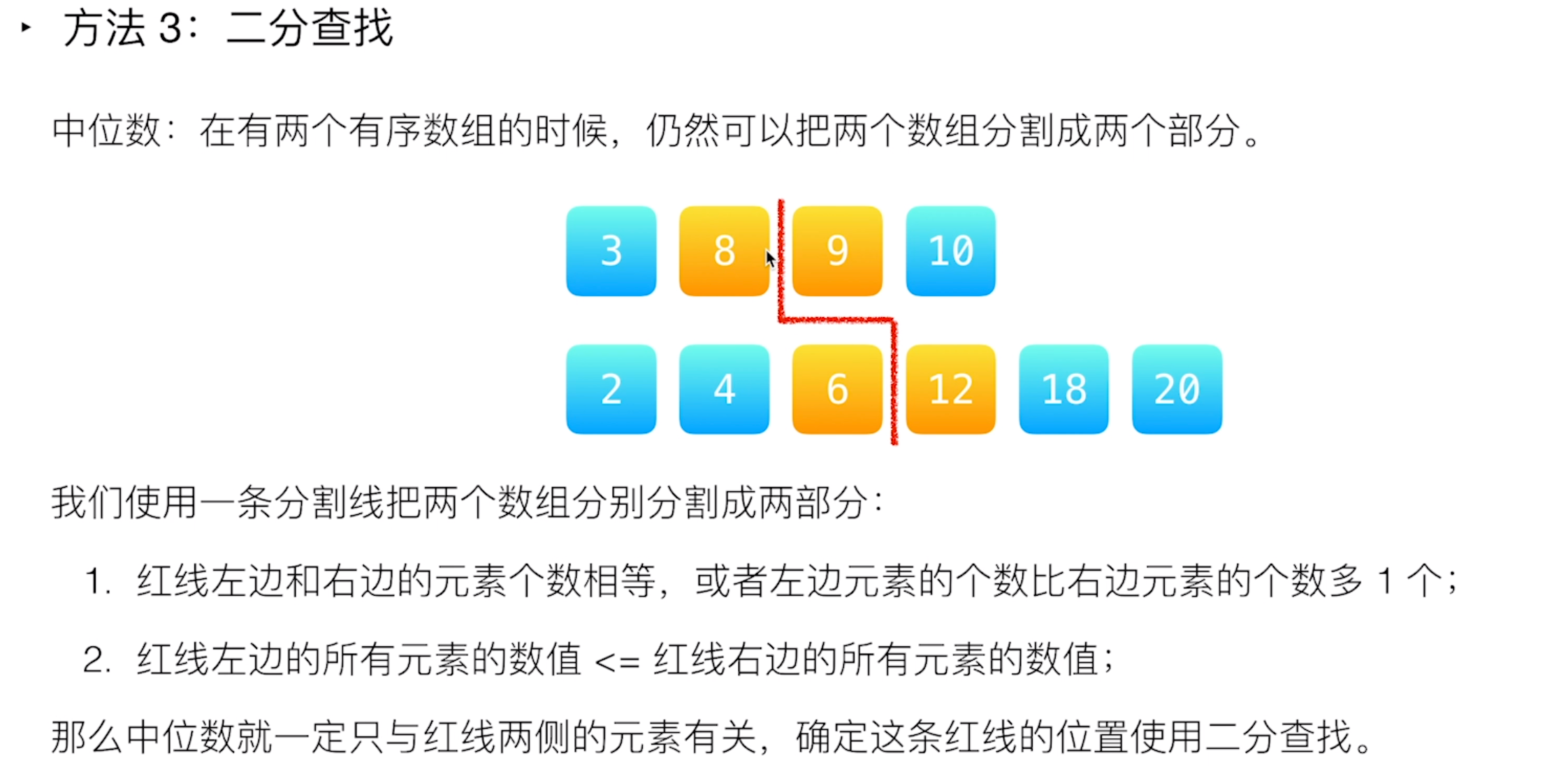
等有一天领悟此题
题解
3 New原理
题目:实现一个new操作符的功能
请利用Ts | Js,实现一个new操作符的功能
分析
new操作符一共分为4步:
- 创建一个对象,并将原型指向构造器的原型
- 纠正创建对象的构造器
- 借用构造函数,去初始化数据
- 返回构造函数返回的对象(如果存在),不存在则返回创建的对象
题解
function MyNew(constructor, ...args) {
const obj = Object.create(constructor.prototype)
obj.constructor = constructor
const result = constructor.apply(obj, args)
console.log('[result]:', result)
console.log('[obj]:', obj)
return typeof result == 'object' ? result : obj
}
使用
class Person {
private name?: string
constructor(name?: string) {
this.name = name
}
}
// function Person(name) {
// this.name = name
// }
// class is only a candy of function
// so it can be applied, although not be invoked
function main() {
const person = MyNew(Person, 'John')
console.log('[person]:', person)
}
main()
Prototype扩展1:Js中 prototype、__proto__、constructor三者之间有什么区别和联系呢?
看下图
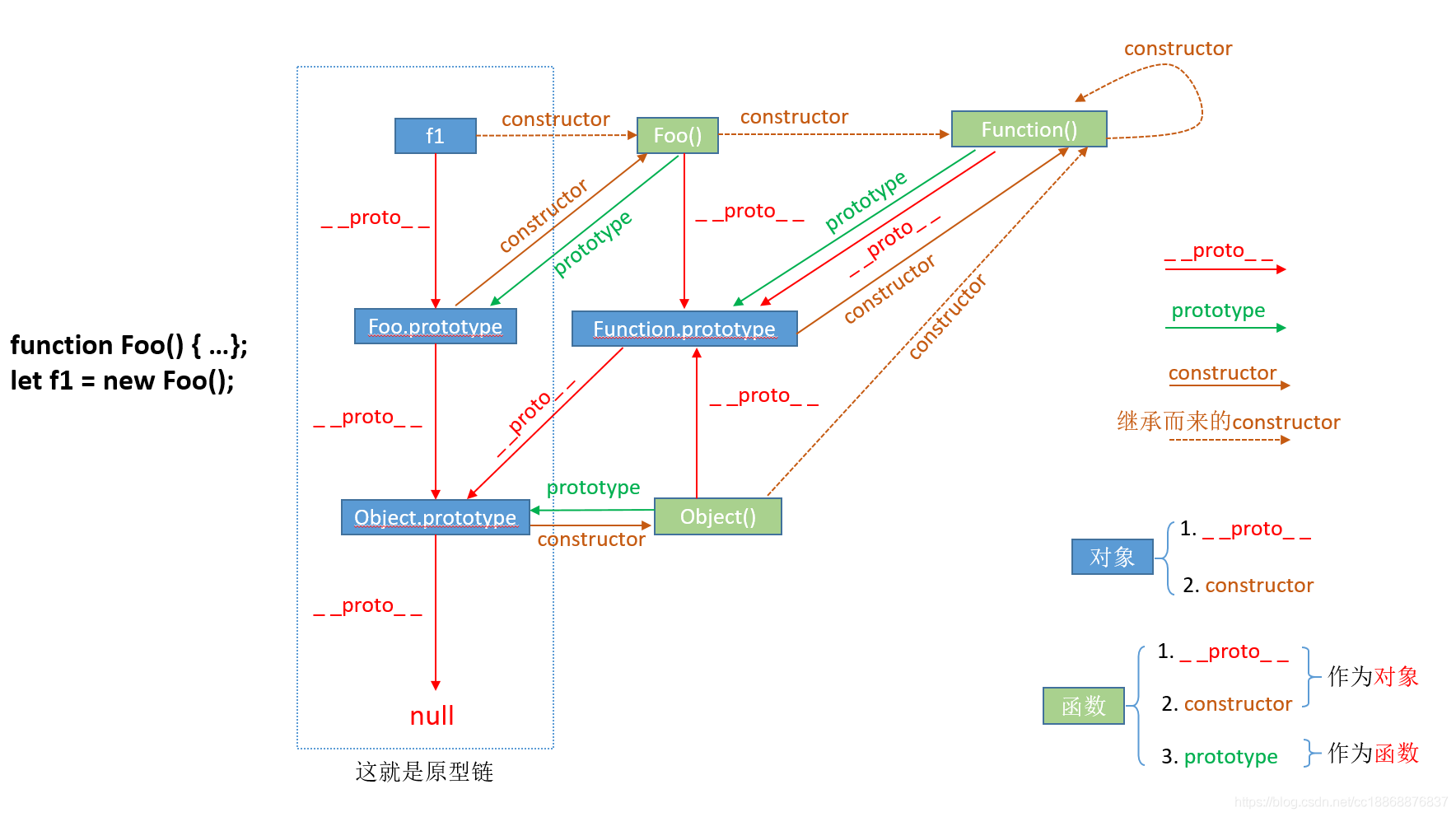
我们只看单独的一个,就比价清楚它们三者的联系了:
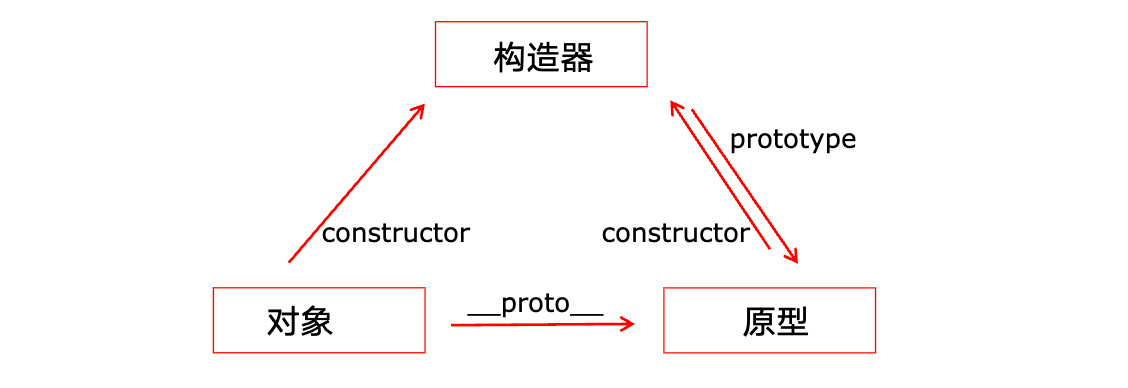
看懂这个图,就可以解决以下问题:
- 为什么Person.prototype.say方法,在person实例上可以调用?
Prototype扩展2:用toString去准确判断数据类型
以下部分代码参考自 lodash 库
const arrayTag = '[object Array]'
const boolTag = '[object Boolean]'
const dateTag = '[object Date]'
const errorTag = '[object Error]'
const mapTag = '[object Map]'
const numberTag = '[object Number]'
const objectTag = '[object Object]'
const regexpTag = '[object RegExp]'
const setTag = '[object Set]'
const stringTag = '[object String]'
const symbolTag = '[object Symbol]'
const weakMapTag = '[object WeakMap]'
function getTag(value) {
if (value == null) {
return value === undefined ? '[object Undefined]' : '[object Null]'
}
return Object.prototype.toString.call(value)
}
使用
const num = 123
if(getTag(num) == numberTag){
console.log('[]:', 'this is a number')
}
// =>
// []: this is a number
4 二分查找法
题目:实现一个二分查找的功能
给定一个有序数组s,请找出数字t的位置,请利用Ts | Js,实现一个二分查找的功能
分析
- 遍历:时间复杂度O(n)
- 二分法:时间复杂度O(logn)
可以从图中看到,logn复杂度到后续越来越快(因为区间越来越小)
题解
function binarySearch(s?: number[], t?: number) {
if (!s || t == undefined) {
return
}
let l = 0,
r = s.length - 1
while (l < r) {
const mid = Math.floor((r + l + 1) / 2)
if (t === s[l] || t === s[r]) {
return t === s[l] ? l : r
}
if (t === s[mid]) {
return mid
} else if (t > s[mid]) {
l = mid + 1
} else {
r = mid
}
使用
function main() {
const s = [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17]
const t = 11
console.log('[]:', binarySearch(s, t))
}
main()
5 算法3.9
题目:146. LRU 缓存机制(opens new window) ( 中等😕 )
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity)以 正整数 作为容量capacity初始化 LRU 缓存int get(int key)如果关键字key存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回-1。void put(int key, int value)如果关键字key已经存在,则变更其数据值value;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组key-value。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过capacity,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。
函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
示例
输入
["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"]
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
输出
[null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]
解释
LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2);
lRUCache.put(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1}
lRUCache.put(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 1
lRUCache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.get(3); // 返回 3
lRUCache.get(4); // 返回 4
分析
两个关键点:
- key-value结构,那么需要哈希表
- 维护一个最近 & 最少的一个结构
- 随意移动、插入
- 随机访问
很明显,难点在于维护这个最近&最少的一种结构,可以想到 栈、队列、链表等数据结构,这里我开始想到了用队列,但后面发现如果要移动元素到顶部,会影响到队列其他元素,无法满足O(n),这时就想到链表,因为链表插入,移除元素,满足O(n)。但还有一个问题,链表如何满足随机访问呢?通过map存节点信息即可快速找到该节点。
题解
class DLinkedNode {
key: number
value: number
prev: DLinkedNode | undefined
next: DLinkedNode | undefined
constructor(key?: number, value?: number) {
this.key = key
this.value = value
}
}
class LRUCache {
private capacity: number
private size: number
private cache = new Map<number, DLinkedNode>()
private head: DLinkedNode
private tail: DLinkedNode
constructor(capacity: number) {
this.capacity = capacity
this.size = 0
this.head = new DLinkedNode()
this.tail = new DLinkedNode()
this.head.next = this.tail
this.tail.prev = this.head
}
get(key: number): number {
const node = this.cache.get(key)
if (node === undefined) {
return -1
} else {
this.moveToHead(node)
return node.value
}
}
put(key: number, value: number): void {
const node = this.cache.get(key)
if (node === undefined) {
// create node
const newNode = new DLinkedNode(key, value)
this.cache.set(key, newNode)
this.addToHead(newNode)
++this.size
if (this.size > this.capacity) {
const last = this.removeTail()
this.cache.delete(last.key)
--this.size
}
} else {
node.value = value
this.moveToHead(node)
}
}
addToHead(node: DLinkedNode) {
// Insert elements in head, first prev, then next
// Insert elements in tail, first next, then prev
node.prev = this.head
node.next = this.head.next
this.head.next.prev = node
this.head.next = node
}
removeNode(node: DLinkedNode) {
node.prev.next = node.next
node.next.prev = node.prev
}
moveToHead(node: DLinkedNode) {
this.removeNode(node)
this.addToHead(node)
}
removeTail() {
const last = this.tail.prev
this.removeNode(last)
// for finding the key, and remove the element in cache
return last
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new LRUCache(capacity)
* var param_1 = obj.get(key)
* obj.put(key,value)
*/
使用
function main() {
const obj = new LRUCache(2)
const param_1 = obj.get(0)
obj.put(0, 1)
const param_2 = obj.get(0)
console.log('[param_1]:', param_1)
console.log('[param_2]:', param_2)
}
main()
6 算法3.10
题目:287.寻找重复数 ( 中等😕 )
给定一个包含 n + 1 个整数的数组 nums ,其数字都在 [1, n] 范围内(包括 1 和 n),可知至少存在一个重复的整数。
假设 nums 只有 一个重复的整数 ,返回 这个重复的数 。
你设计的解决方案必须 不修改 数组 nums 且只用常量级 O(1) 的额外空间。
示例
示例1
输入:nums = [1,3,4,2,2]
输出:2
示例2
输入:nums = [3,1,3,4,2]
输出:3
分析
以下方法空间复杂度都是O(n),满足题目要求
暴力法
双层for循环,按个按个比较,如果相等 即找到该元素
- 时间复杂度O(n^2)
二分法
根据这个图的思路,然后在纸上画一画,就明白了
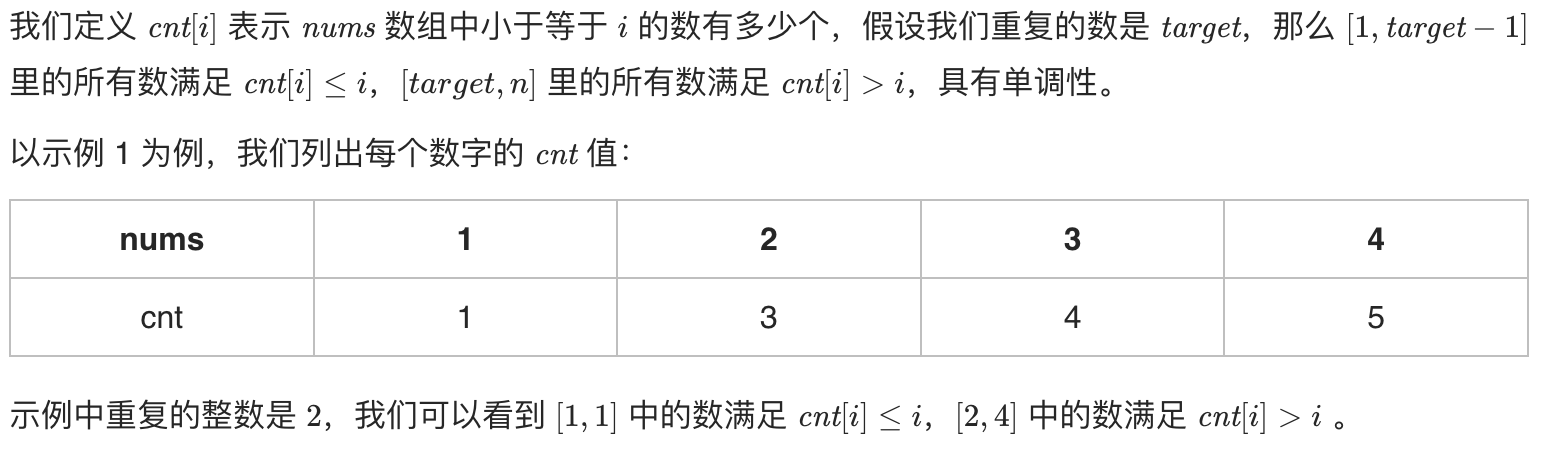
这个题目条件很苛刻:其数字都在
[1, n]范围内(包括1和n),而且只有 一个重复的整数所以才可以这样操作,下面的快慢指针也是如此
时间复杂度O(n*logn)
快慢指针
建议参考:二分法&快慢指针
- 时间复杂度O(n)
题解
二分法
function findDuplicate(nums: number[]): number {
const len = nums.length
let l = 0,
r = len - 1,
ans = -1
while (l <= r) {
const mid = Math.floor((r + l) / 2)
let cnt = 0
for (let i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
if (nums[i] <= mid) {
++cnt
}
}
console.log('[]:', r, mid, l, cnt)
if (cnt <= mid) {
l = mid + 1
} else {
r = mid - 1
ans = mid
}
}
return ans
}
快慢指针
function findDuplicate111(nums: number[]): number {
let slow = 0,
fast = 0
// Find the entrance to the ring
while (true) {
slow = nums[slow]
fast = nums[nums[fast]]
if (fast == slow) {
break
}
}
// Find the element, based on the entry
let find = 0
while (true) {
find = nums[find]
slow = nums[slow]
if (find == slow) {
break
return find
}
扩展1:141. 环形链表 ( 简单😄 )
扩展2:142. 环形链表 II ( 中等😕 )
7 订阅-发布模式
题目:请利用 Ts | Js 实现一个订阅-发布模式(或者称为发布-订阅模式)
分析
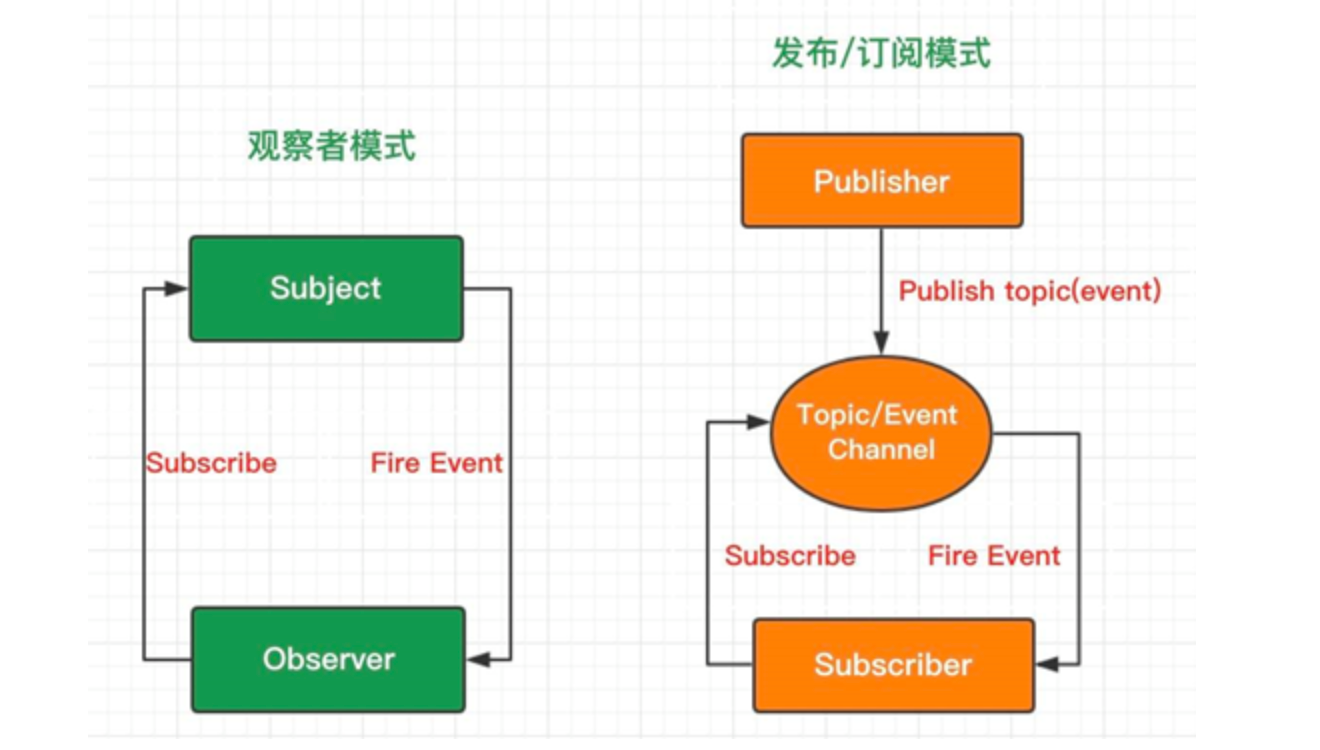
注意区分 观察者模式 和 订阅-发布模式,详见 观察者模式与订阅发布模式的区别
由下图可以发现,订阅-发布模式多了一个 中间人,负责订阅和发布
题解
class PubCenter {
private subscribers: {
[type: string]: ((...args: any) => void)[]
} = {}
subscribe(type: string, fn: any) {
const topic = this.subscribers[type]
if (topic) {
topic.push(fn)
} else {
this.subscribers[type] = [fn]
}
}
publish(msg: any, type?: string) {
if (!type) {
Object.keys(this.subscribers).forEach((type) => {
this.publish(msg, type)
})
} else {
const topic = this.subscribers[type]
topic?.forEach((x) => x && x(`type:${type}, msg:${msg}`))
}
}
unsubscribe(type: string, fn: any) {
if (!type || !fn) return
const existIndex = this.subscribers[type]?.indexOf(fn)
if (existIndex != -1) {
this.subscribers[type].splice(existIndex, 1)
}
}
clear(type?: string) {
if (!type) {
this.subscribers = {}
} else {
this.subscribers[type] = this.subscribers[type] ? [] : undefined
}
}
}
使用
function main() {
const pubCenter = new PubCenter()
const fn1 = (msg) => {
console.log('[fn1 receive msg]:', msg)
}
const fn2 = (msg) => {
console.log('[fn2 receive msg]:', msg)
}
const fn3 = (msg) => {
console.log('[fn3 receive msg]:', msg)
}
pubCenter.subscribe('SMS', fn1)
pubCenter.subscribe('SMS', fn2)
pubCenter.subscribe('SMS', fn3)
pubCenter.subscribe('QQ', fn1)
pubCenter.publish('hello, everyone111')
console.log('[-----------unsubscribe fn2 SMS--------------]:')
pubCenter.unsubscribe('SMS', fn2)
pubCenter.publish('hello, everyone222')
console.log('[-----------clear all SMS--------------]:')
pubCenter.clear('SMS')
pubCenter.publish('hello, everyone333')
}
main()
输出
[fn1 receive msg]: type:SMS, msg:hello, everyone111
[fn2 receive msg]: type:SMS, msg:hello, everyone111
[fn3 receive msg]: type:SMS, msg:hello, everyone111
[fn1 receive msg]: type:QQ, msg:hello, everyone111
[-----------unsubscribe fn2 SMS--------------]:
[fn1 receive msg]: type:SMS, msg:hello, everyone222
[fn3 receive msg]: type:SMS, msg:hello, everyone222
[fn1 receive msg]: type:QQ, msg:hello, everyone222
[-----------clear all SMS--------------]:
[fn1 receive msg]: type:QQ, msg:hello, everyone333
8 算法3.11
题目:974. 和可被 K 整除的子数组 ( 中等😕 )
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,返回其中元素之和可被 k 整除的(连续、非空) 子数组 的数目。
子数组 是数组的 连续 部分。
示例
示例1
输入:nums = [4,5,0,-2,-3,1], k = 5
输出:7
解释:
有 7 个子数组满足其元素之和可被 k = 5 整除:
[4, 5, 0, -2, -3, 1], [5], [5, 0], [5, 0, -2, -3], [0], [0, -2, -3], [-2, -3]
示例2
输入: nums = [5], k = 9
输出: 0
分析
暴力法 + 哈希表
双层循环,哈希表中存之前的和,依次判断与k的余数,如果为0,则为答案,将答案累加即可
- 时间复杂度O(n^2),空间复杂度O(n)
前缀和 + 逐一统计
这是LeetCode的一段重要的阶梯思路:

问题一:为什么要将
负余数纠正呢?(sum % k + k) % k纠正算法又是怎么来的呢?时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
题解
function subarrayDivByK(nums: number[], k: number): number {
const len = nums.length
const map = new Map<number, number>()
map.set(0, 1)
let sum = 0,
ans = 0
for (let i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
sum += nums[i]
let mod = ((sum % k) + k) % k
// mod = mod < 0 ? -mod : mod
const same = map.get(mod) ?? 0
ans += same
map.set(mod, same + 1)
}
return ans
}
使用
function main() {
const nums = [4, 5, 0, -2, -3, 1]
const k = 5
console.log('[]:', subarrayDivByK(nums, k))
}
main()
export {}
问题解答
问题一:为什么要将 负余数 纠正呢?(sum % k + k) % k 纠正算法又是怎么来的呢?
因为余数不应该为负数,-1和1 与2的余数是一致的,都为1
9 Event类
题目:请用Ts | Js实现一个Event类
Event类具有如下功能:
- 注册事件
- 触发事件(一次,多次)
- 注销事件
分析
Event与发布-订阅模式类似,区别为前者为 一对一,而后者为 一对多
题解
class EventBus {
private cache: {
[type: string]: ((...args: any) => void)[]
} = {}
on(type: string, fn: any) {
const fns = this.cache[type]
if (fns) {
fns.push(fn)
} else {
this.cache[type] = [fn]
}
return this
}
once(type: string, fn: any) {
const wrapped = (...args) => {
fn.apply(null, args)
this.off(type, wrapped)
}
return this.on(type, wrapped)
}
emit(type: string, ...args: any) {
const fns = this.cache[type]
fns && fns.forEach((fn) => fn && fn.apply(null, args))
return this
}
off(type: string, fn: any) {
const fns = this.cache[type]
if (!fns) return this
const found = fns.indexOf(fn)
if (found != -1) {
fns.splice(found, 1)
}
return this
}
clear(type?: string) {
if (!type) {
this.cache = {}
} else {
this.cache[type] = []
}
return this
}
}
使用
function main() {
const bus = new EventBus()
const eventName = 'UPDATE'
const arg = 'hello'
const update = (arg) => {
console.log('[]:', arg)
}
bus.on(eventName, update)
bus.on(eventName, update)
bus.on(eventName, update)
bus.emit(eventName, arg)
console.log('[---------off one------------]:')
bus.off(eventName, update).emit(eventName, arg)
console.log('[---------clear UPDATE------------]:')
bus.clear(eventName)
bus.emit(eventName, arg)
console.log('[---------once------------]:')
bus.once(eventName, update)
bus.emit(eventName, arg)
bus.emit(eventName, arg)
}
main()
export {}
输出
[]: hello
[]: hello
[]: hello
[---------off one------------]:
[]: hello
[]: hello
[---------clear UPDATE------------]:
[---------once------------]:
[]: hello
参考
[1] 手写 Event 类.https://2heal1.github.io/interviewCoding/%E6%89%8B%E5%86%99Event%E7%B1%BB.html#%E6%89%8B%E5%86%99-event-%E7%B1%BB
10 Reflect
介绍
首先明确,Reflect是一个 对象,字面意思为反射。它的主要作用是代替JS原有的方法或者操作符,例如:
- Object上操作对象的方法(区别见[1])
- in、delete操作符 =>>
Reflect.has、Reflect.deleteProperty
所以,可以认为Reflect是一个规范化的对象,用于去操作对象
其次,Reflect上的常见方法,也对应着代理中handler对象上的方法
❗ 注意Object是一个函数构造器,而Reflect是一个对象
其他介绍,详见 Reflect
[1] 比较 Reflect 和 Object 方法.https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Reflect/Comparing_Reflect_and_Object_methods
11 Vue响应式原理-Vue2/Vue3
TODO
12 实现Array.prototype.reduce
题目:实现Array.prototype.reduce
请使用Ts | Js实现Array.prototype.reduce方法
分析
注意:
- 注意this指向,不要使用箭头函数去实现myReduce,否则this指向当前上下文(我的代码中是window)
题解
TODO:边界条件处理
// @ts-ignore
Array.prototype.myReduce = function (fn: (prev: any, curr: any, index: number) => any, initialValue: any) {
// @ts-ignore
const len = this.length
let prev = initialValue
for (let i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
// @ts-ignore
prev = fn(prev, this[i], i)
}
return prev
}
使用
function main() {
const arr = [1, 2, 3]
// @ts-ignore
const res = arr.myReduce((memo, curr) => {
memo = memo + curr
console.log('[memo]:', memo)
return memo
}, 0)
console.log('[]:', res)
}
main()
export {}
13 Nginx反向代理配置
server {
listen 80;
server_name _;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/cert/1_gincool.com_bundle.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/cert/2_gincool.com.key;
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name gincool.com;
#root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
location /hapvac/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3040/;
}
location / {
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_pass http://localhost:3071;
proxy_read_timeout 90;
proxy_redirect http://localhost:3071 https://gincool.com;
}
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/gincool.com/fullchain.pem; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/gincool.com/privkey.pem; # managed by Certbot
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name api.gincool.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3050/;
}
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/gincool.com/fullchain.pem; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/gincool.com/privkey.pem; # managed by Certbot
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name dashboard.gincool.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3051/;
}
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/gincool.com/fullchain.pem; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/gincool.com/privkey.pem; # managed by Certbot
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name api-yuecode.gincool.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3060/;
}
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/gincool.com/fullchain.pem; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/gincool.com/privkey.pem; # managed by Certbot
}